Exponents, also known as powers or indices, are a fundamental concept in mathematics. It plays a crucial role in various fields, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus. An exponent represents how many times a number, called the base, is multiplied by itself. To solve exponents involves understanding the properties of exponents, simplifying expressions, and performing operations with exponential terms. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of solving exponent problems using maths.ai as a teaching tool.
Understanding Exponents
Before we delve into solving exponents problems, let’s review the basics of exponents.
An exponent is usually written as a superscript number next to the base. For example, in the expression 2^3, 2 is the base, and 3 is the exponent. This means that 2 is multiplied by itself three times: 2 * 2 * 2 = 8.
Example 1: Simple Exponentiation
Let’s solve the problem: 4^2.
Step 1: Identify the base and the exponent.
Base: 4
Exponent: 2
Step 2: Apply the exponentiation rule.
4^2 = 4 * 4 = 16
Exponent Properties
Understanding exponent properties is essential for solving more complex exponent problems.
Property 1: Product of Powers
a^m * a^n = a^(m + n)
This property states that when you multiply two powers with the same base, you can add their exponents.
Example 2: Product of Powers
Solve the problem: 3^4 * 3^2.
Step 1: Identify the base and the exponents.
Base: 3
Exponent 1: 4
Exponent 2: 2
Step 2: Apply the product of powers property.
3^4 * 3^2 = 3^(4 + 2) = 3^6 = 729
Property 2: Quotient of Powers
a^m / a^n = a^(m – n)
This property states that when you divide two powers with the same base, you can subtract their exponents.
Example 3: Quotient of Powers
Solve the problem: 5^7 / 5^4.
Step 1: Identify the base and the exponents.
Base: 5
Exponent 1: 7
Exponent 2: 4
Step 2: Apply the quotient of powers property.
5^7 / 5^4 = 5^(7 – 4) = 5^3 = 125
Property 3: Power of a Power
(a^m)^n = a^(m * n)
This property states that when you raise a power to another power, you can multiply the exponents.
Example 4: Power of a Power
Solve the problem: (2^3)^4.
Step 1: Identify the base and the exponents.
Base: 2^3
Exponent: 4
Step 2: Apply the power of a power property.
(2^3)^4 = 2^(3 * 4) = 2^12 = 4096
Simplifying Exponential Expressions
Simplifying exponential expressions involves applying the properties of exponents to combine or rewrite terms for easier computation.
Example 5: Simplifying Exponential Expressions
Simplify the expression: 2^5 * 2^8 / 2^3.
Step 1: Identify the base and the exponents.
Base: 2
Exponent 1: 5, Exponent 2: 8, Exponent 3: 3
Step 2: Apply the properties of exponents.
2^5 * 2^8 / 2^3 = 2^(5 + 8 – 3) = 2^10 = 1024
Operations with Exponential Terms
Performing operations with exponential terms involves applying the properties of exponents while considering addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Example 6: Operations with Exponential Terms
Solve the expression: (4^3 * 4^2) / 4^4 + 4^1.
Step 1: Identify the base and the exponents for each term.
Term 1: 4^3 * 4^2,Term 2: 4^4, Term 3: 4^1
Step 2: Simplify each term using the properties of exponents.
Term 1: 4^3 * 4^2 = 4^(3 + 2) = 4^5, Term 2: 4^4, Term 3: 4^1
Step 3: Combine the terms using addition and subtraction.
(4^5 * 4^4) / 4^4 + 4^1 = 4^5 + 4^1
Step 4: Calculate the final result.
4^5 + 4^1 = 1024 + 4 = 1028
Exponents are a fundamental concept in mathematics that allows us to represent repeated multiplication in a concise form. By understanding the properties of exponents, simplifying expressions, and performing operations with exponential terms, you can confidently tackle various exponent problems. Remember to apply the rules systematically, and when in doubt, use tools maths.ai to assist you in your journey towards mastering exponents. With practice and a clear grasp of exponent principles, you’ll be well-equipped to solve more complex maths problems that involve exponents.
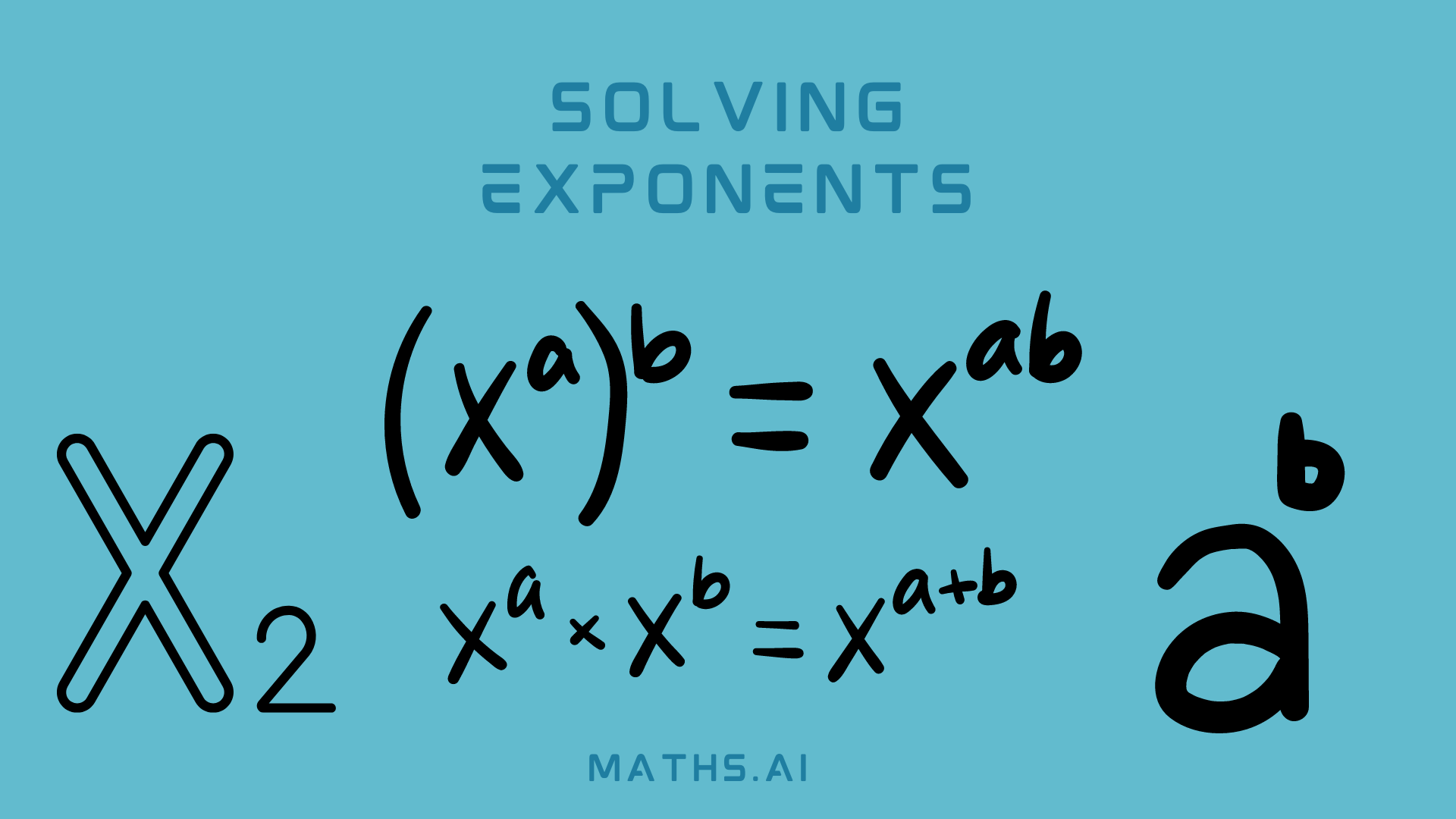

3 Comments