logarithms – a mathematical tool that unveils the secrets within exponential relationships. Whether you’re diving into advanced algebra or preparing for the wonders of calculus, understanding logarithms is like acquiring a powerful key to decipher complex mathematical puzzles. Join us on this journey as we demystify logarithms and discover their role in unlocking the magic of exponents.
Check out calculus, before understanding logarithms
The Essence of Logarithms:
1. Defining Logarithms:
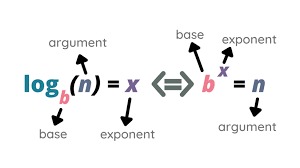
At its core, a logarithm is the inverse operation of exponentiation. If by=x, then the logarithm base b of x is y, expressed as log(x)=y.
2. Key Terminology:
- Base (b): The number to which the logarithm is applied.
- Argument (x): The number for which the logarithm is being calculated.
- Exponent (y): The power to which the base is raised to get the argument.
Properties of Logarithms:
1. Product Rule:
logb(mn)=logb(m)+logb(n)
2. Quotient Rule:
logb(nm)=logb(m)−logb(n)
3. Power Rule:
logb(mn)=n⋅logb(m)
Common Logarithms and Natural Logarithms:
1. Common Logarithms (Base 10):
Written as log(x), where the base is 10. It’s commonly used in various fields, especially in technology and science.
2. Natural Logarithms (Base �e):
Denoted as )ln(x), where e is Euler’s number (approximately 2.71828). Natural logarithms frequently appear in calculus and mathematical analysis.
Solving Exponential Equations:
1. Logarithmic Form:
Exponential equations by=x can be rewritten in logarithmic form as logb(x)=y. Logarithms help solve for the unknown exponent.
2. Application in Real-World Scenarios:
Logarithms are used in various fields, from finance (calculating compound interest) to biology (measuring population growth).
Graphical Representation:
1. Logarithmic Graphs:
Logarithmic functions exhibit distinct characteristics in their graphs, including asymptotes and unique shapes.
2. Understanding Logarithmic Scales:
Logarithmic scales are commonly used in data representation, allowing for a clear visualization of exponential growth or decay.
Advanced Concepts:
1. Logarithmic Differentiation:
An advanced calculus technique that leverages logarithmic properties to simplify complex differentiation problems.
2. Applications in Computer Science:
Logarithms play a vital role in algorithms and computational complexity, influencing the efficiency of various algorithms.